Introduction
{getToc} $title={Table of Contents}
- Polyamides are polymers whose monomeric units are joined by the amide (-NH-CO-) linkage (at least 85%).
- They contain aliphatic or cyclo-aliphatic units, often known as nylons.
- Polyamides are synthesized by a condensation reaction between diamine and diacid, where the repeating units are held together by amide links.
- In 1939, the first polyamide in the USA was produced from adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine named polyamide 66.
- In 1938, German caprolactam was polymerized to form polyamide 6 (Nylon 6).
Synthesis of Nylon 66
 |
| Synthesis of Nylon 66 |
Synthesis of Nylon 6
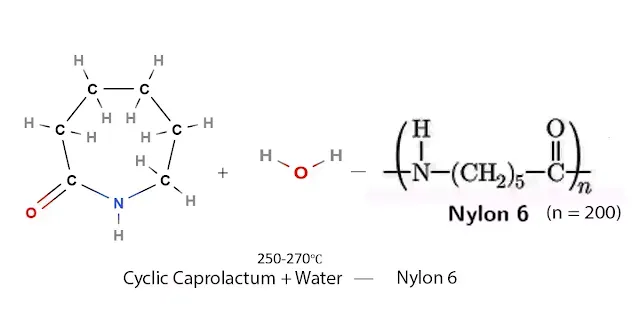 |
| Synthesis of Nylon 6 |
Extrusion of Nylon
- Polyamide fibers/filaments are melt spun.
- Dry N2 is used to prevent oxidation.
- Extrusion temperature Nylon 66 (280- 290℃), Nylon 6 (250-270℃).
- Spinneret holes dia 0.1-0.4 mm.
- Extrusion velocity is normally 1000-1200 meters/min.
- After extrusion, it passes through a cooling chamber almost 5 meters long.
- The filaments are then moisturized through steam or spin finish to absorb a small amount of water (MR% 4.0-4.5).
- The filaments are drawn at a drawing ratio of 4-5 in the cold drawing method for apparel used and carpets.
- Stronger yarns are required for demanding applications drawn at a higher temperature, then texturized, and finally heat set.
- Heating-Nylon 66 (180-200℃)-Nylon 6 (160-180℃) in the presence of steam.
- Induce the annealing process.
- The estimated polymer length is 90-140 nm.
- The estimated polymer thickness is 0.3 nm.
Properties of Nylon
End Uses of Nylon
- Swimwear, skiwear, sportswear, lingerie.
- Extensively used as carpet fibers.
- Wool/Nylon (80: 20) blend.
- High-tenacity tire cord, adhere to rubber.
- Reinforced rubber in drive belts, and conveyor vehicle airbags.
Tags
Synthetic Fibers